India

BOMBAY,
situated on a narrow peninsula, is a major port and the ocean gateway to western India. It is also a financial, industrial and commercial center. Bombay was acquired by the Portuguese in 1534, ceded to the British in 1661, and became the headquarters of the British East India Company in 1672. It became the country's largest distributing center after the opening of India's first railroad in 1853 and the Suez Canal in 1869. A horse tramway opened on May 9, 1874, and an electric tram system, using single-deck cars, on May 7, 1907. Double-deck trams appeared in September 1920 and by 1935 there were 433 trams running on 47 km of track. A brochure published by the tramway company shows a typical car. The system closed on March 31, 1964.

CALCUTTA,
the capital of West Bengal, is located in northeast India on the Hooghly River and is one of the world's busiest ports. The city was the capital of British India from 1773 until 1912 and was renowned as the "wickedest city in the world." The British established a trading center in 1690 and, when the city was captured by the Nawab of Bengal in 1756, British forces were imprisoned in the infamous Black Hole. A horse tram system opened in January 1881, after a premature experiment in 1873, and a steam tramway line in 1882. Electric trams began running on March 27, 1902 and by 1921 there were 56 km of track and 512 cars in service. The postcard shows a street scene in the business district. The tram system is still operating today.

CAWNPORE
is located in northern India on the right bank of the Ganges and is an important rail junction and industrial center. It was garrisoned by British troops in 1778 and was the site of a Sepoy Mutiny massacre by Nana Sahib in July 1857. The tram system opened in June 1907 and closed on May 16, 1933. There were 4 miles of track and 20 single-deck open trams. The single line connected the railway station with Sirsaya Ghat on the banks of the Ganges. Photographs of Cawnpore trams are very rare.
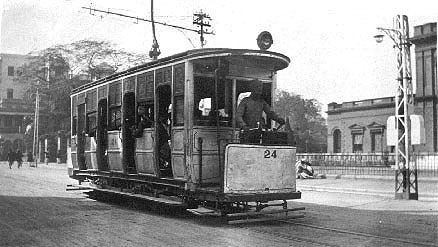
DELHI,
on the west bank of the Yamuna River in northern India, consists of Old and New Delhi. Old Delhi is an important manufacturing, rail and trade center built around the Red Fort, site of the famous Peacock Throne. South of the city walls is New Delhi, a planned city with wide boulevards and imposing government buildings, capital of India since 1912. Delhi has controlled northern India since the 13th Century. The British took the city in 1803 from the Mogul emperors and Coronation Durbars were held in 1903 and 1911. The tram system opened on March 6, 1908 and by 1921 there were 15 km of track and 24 cars. The system closed ca. 1963. This rare postcard shows a typical open car.

MADRAS,
on the Coromandel Coast, is the main port of southeast India and a rail and manufacturing center. The city was founded in 1639 by the British East India Company as Fort St. George, and is widely dispersed with broad avenues radiating from the fort area. The electric tram system, which opened on May 7, 1895, was the first in India. The original conduit system was replaced by an conventional overhead wire system after a series of destructive monsoons. By 1921 there were 24 km of track and 97 cars, one of which is shown on this postcard. The system closed on April 12, 1953.